A Comprehensive Guide to Data Pre-Processing in Machine Learning
Introduction
Data pre-processing is essential to ensure that different algorithms can be effectively applied, stored, and retrieved for later use. The steps below will guide you through the process of data pre-processing.
Section A: Building Basics
“Build the basics strong, and you’ll go far without looking back.”
1. Features
Features are generally the columns in which different data is based. For example, in a company employee table, data like name, age, experience, salary, etc., are features that are shared among the employees to save that data in the database.
2. Independent Variables
These are variables that are independent of anything. For example, in the employee table mentioned earlier, name and age could be independent variables.
3. Dependent Variables
Dependent variables rely on independent ones. For example, the salary column could be dependent on factors such as experience and age.
4. Cleaning the Dataset
Cleaning datasets can be challenging, but it is crucial for improving the data quality. There are primarily two approaches:
4.1 Removing the Missing Row
If you have a large dataset, you can afford to remove rows with missing data using a Python library you are comfortable with.
4.2 Replacing with the Averages
When data is limited and important, you can replace missing values with the average of the column.
Note: Giving random or constant values to missing rows can increase the bias in the results.
5. Encoding Categorical Variables
For datasets with categorical variables, such as employee designations like IT, Business, and Marketing, encoding is necessary.
5.1 One Hot Encoding
Use one-hot encoding to convert categorical variables into vectors. For example, you can represent categories as [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0], and [1, 0, 0] in separate columns.
6. Training and Testing Set
The dataset should be split into a training set (used for training the model) and a testing set (used for validation). A common split is 80% for training and 20% for testing.
7. Feature Scaling
Feature scaling is essential for ensuring that features are on the same scale, which aids in comparison and improves model accuracy.
Types of Feature Scaling
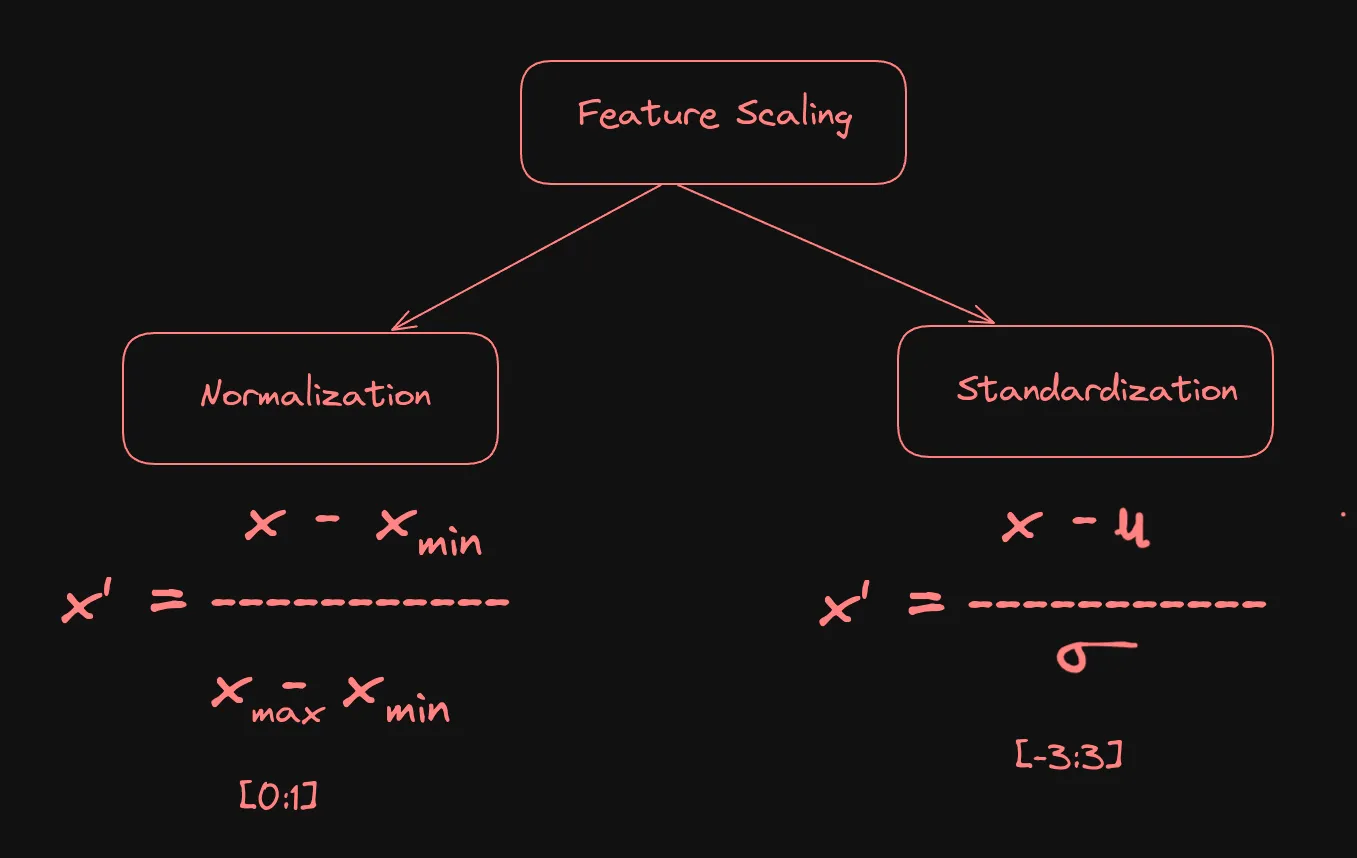
7.1 Normalization
Normalization is a technique used to scale numerical features between a specific range, usually between 0 and 1. This is helpful when different features have different scales, and it’s essential to compare or group them together. Normalization is commonly used when dealing with categorical data, such as image or audio data, where the values can vary significantly.
The formula for normalization is:
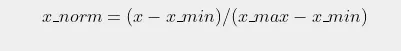
Where x is the original value, x_min is the minimum value in the dataset, x_max is the maximum value, and x_norm is the normalized value.
By using normalization, we can ensure that all features are on the same scale, which can improve the accuracy of machine learning models and help in better data comparison.ntly.
7.2 Standardization
Standardization does not have a fixed range of values. The resulting values follow a standard normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. This means that the values can be any real number, but they will be centered around 0 and will have a relatively small spread. In practice, the values obtained after standardization can range from negative infinity to positive infinity, although they are most likely to fall within a few standard deviations of the mean. For example, if the standard deviation is 1, then 68% of the data will fall within one standard deviation of the mean (-1 to +1), 95% will fall within two standard deviations (-2 to +2), and 99.7% will fall within three standard deviations (-3 to +3).
Section B: Practical
1. Importing the Libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import csv
Let’s assume our dataset is like this:
| Designation | Months to Revenue | Revenue Generated (in thousands) | Revenue Profitable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing | 5 | 125 | Yes |
| IT | 2 | 160 | Yes |
| Business | Nan | 120 | No |
| Marketing | 4 | 150 | Yes |
| IT | 6 | 105 | No |
| Business | 3 | Nan | Yes |
| Marketing | 8 | 80 | No |
| IT | 5 | 125 | Yes |
| Business | 4 | 130 | No |
| Marketing | 3 | 210 | Yes |
2. Reading the CSV File
df = pd.read_csv("your_dataset_name.csv")
df
3. Splitting to X and Y
Y is the Output By looking at the dataset, we can see that Revenue Profitable column is the output that we want to predict. and X are the independent variables of the remaining columns.
X = df.iloc[:,:-1].values
Y = df.iloc[:, -1].values
4. Handling the Missing Data
Since we have a small dataset, we can’t afford to drop any of the rows with missing data, so we are filling that in with the averages.
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=np.nan, strategy='mean')
imputer.fit(X[:, 1:3])
X[:, 1:3] = imputer.transform(X[:, 1:3])
5. Encoding Categorical and Independent Variables
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
ct = ColumnTransformer(transformers=[('encoder', OneHotEncoder(), [0])], remainder='passthrough')
X = np.array(ct.fit_transform(X))
6. Encoding the Dependent Variable
Since it has only two labels, Yes or No. So, we are applying this LabelEncoder to the dependent variable.
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
le = LabelEncoder()
Y = le.fit_transform(Y)
7. Splitting the Dataset into Training and Testing Set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2)
8. Applying Feature Scaling
We don’t need to apply the feature scaling to the categorical variables that we encoded earlier; it can make those worse. We generally do feature scaling to keep the same scale overall. We need to apply the same transform to the train as well as the test.
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train[:,3:] = sc.fit_transform(X_train[:,3:])
X_test[:,3:] = sc.transform(X_test[:,3:])
Conclusion
Data pre-processing is a crucial step in the data science pipeline. It ensures that data is clean, well-formatted, and ready for analysis, which improves the performance of machine learning models. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can now transform raw data into a structured format that is suitable for various analytical tasks. If you really loved this, be sure to follow me, and thanks for reading. Have a great day.
